Springtime and New Ideas
Where would we be without a proper order of things, eh?
Chronology matters. There’s a rhythm to these experiences – about two weeks apart, like the quiet beat of an unseen clock somewhere behind the world. Each event linked like pearls on a string, sequenced by something larger than chance.
Log: Jan – Mar 1986 (~ 2 week sequence)
Jan 14: A lucid dream of the Challenger disaster.
Jan 28: The Challenger exploded, confirming the dream.
Feb 10-12: A vision of a cosmic torus; a glimpse into the structure of the universe.
Feb 23: A life-changing UFO sighting over Galway Bay
Mar 9: Received a “Psychic Mayday,” a distress signal from an unknown consciousness.
The story didn’t begin with the UFO. That was only the flash at the surface.
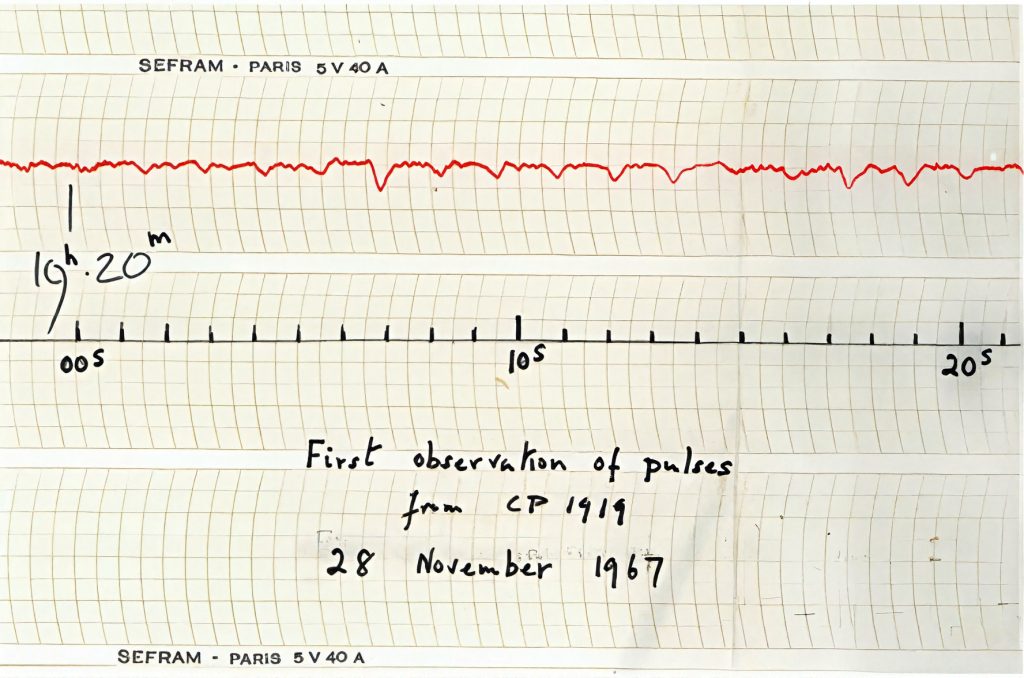
I can still recall, with a clarity that startles me, the night I dreamed of the Challenger disaster – two weeks before it happened, around the fourteenth of January. The images were unmistakable: fire, falling light, a silence that felt endless.
Then came January 28 1986. The dream stepped into daylight. The shuttle broke apart above Florida, and for a moment the whole planet seemed to hold its breath.
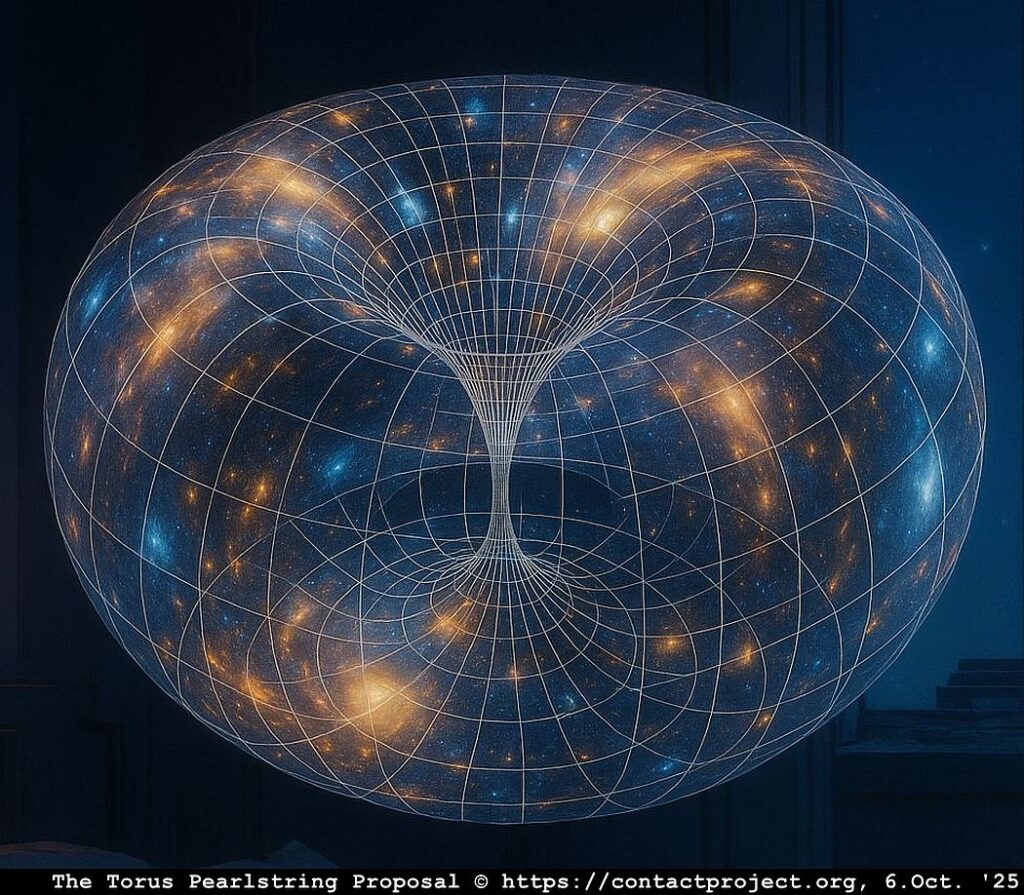
Two weeks later – around February 10th to 12th – I had what I can only call a vision of the cosmos: a torus of living light, immense yet intimate, turning slowly as though revealing the hidden architecture of reality itself.
Not spherical as Einstein imagined, but toroidal: a horn‑torus, a donut universe. And two weeks after that, on February 23rd, came the UFO over Galway Bay.
My dreams and visions weren’t caused by the UFO; if anything, the sighting seemed to answer them, echoing back through whatever channels link mind, matter and time. Each event felt like a note in a larger composition, a sequence strung together by something more deliberate than chance.
Life, of course, went on. I started my own business as a self-employed electrician – rewiring centuries-old cottages, fixing ovens, grounding myself in circuits I could actually hold. Yet something in me had changed. The dream, the vision, the sighting – they had opened a circuit of their own.
The Torus‑Pearlstring Proposal

In the months that followed, I rented an IBM wheelwriter to capture the flood of thoughts, diagrams, and theories that filled my head. I titled the resulting manuscript The Torus–Pearlstring Proposal.
The pages are long lost now, but the journey they began – the search to understand that hidden rhythm, the universe as a coupled system – has never really ended. A torus, not a sphere: energy circulating endlessly, like breath.

A pattern without beginning or end, feeding back through itself in perfect balance – perhaps the same pulse that linked dream, vision, and sighting, looping through consciousness like current through a circuit. For safekeeping I left a copy of the 88 page manuscript with the Ministry of Defense, department SY252, in London, Whitehall in 1987.
If I can ever retrieve it remains to be seen.
The Foghorn Emblem – Contact Project Symbol
One of the diagrams in that manuscript was peculiar: a minimalist black-and-white graphic of three geometric shapes on a white background: two opposing triangles meeting at a vertical bar.
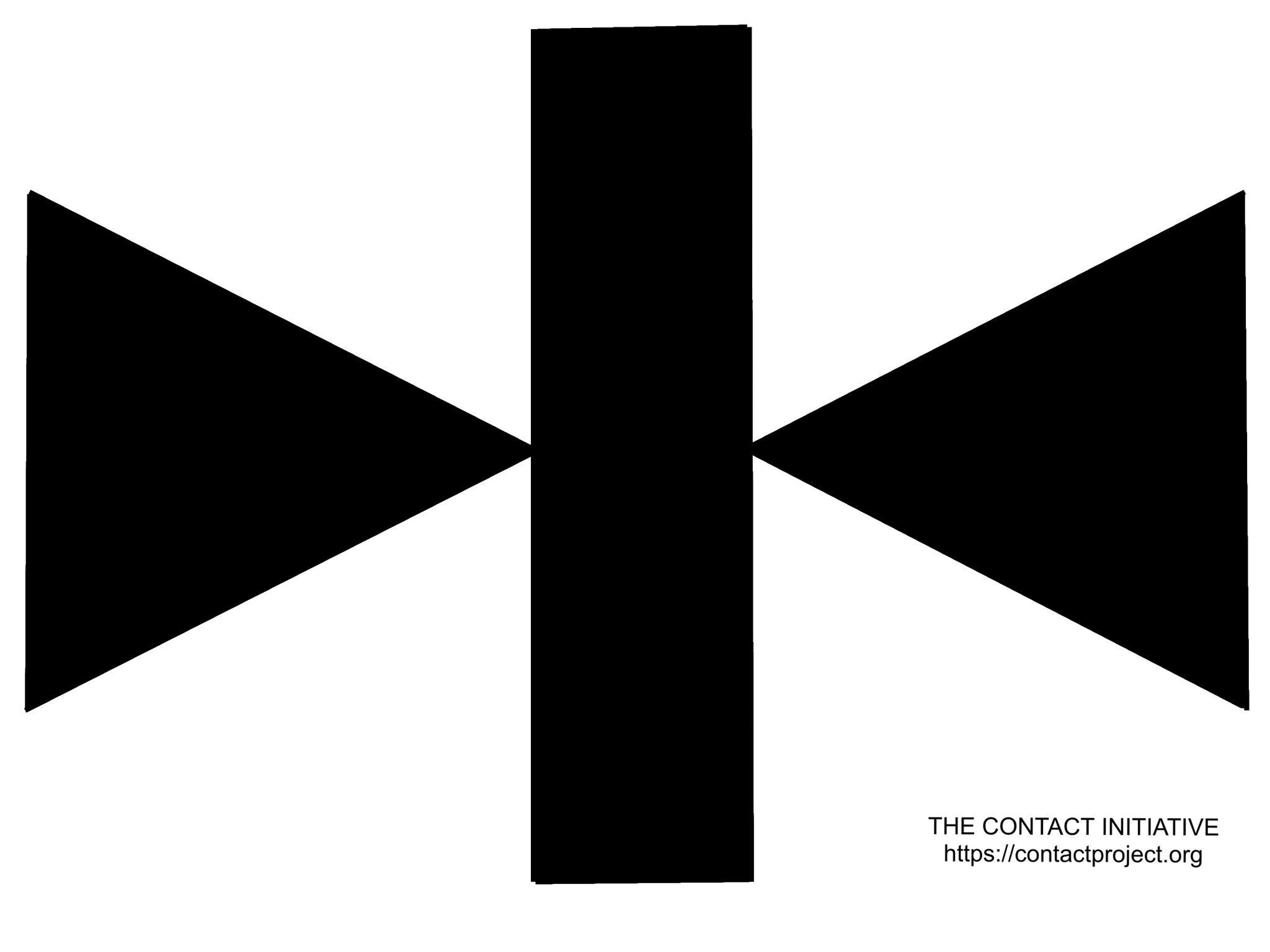
It became the Contact Project “Foghorn Emblem”: Two opposing triangles converge on a central pillar, resembling acoustic horns – perhaps one emitting, one receiving – joined by the conduit of translation. In the language of SETI, it evokes dialogue between signal and interpreter, sender and receiver, civilization and cosmos.
It evokes a cosmic foghorn, a beacon of patterned intent calling through the static of space. It represents the symmetry of sender and receiver, the moment when listening becomes dialogue.
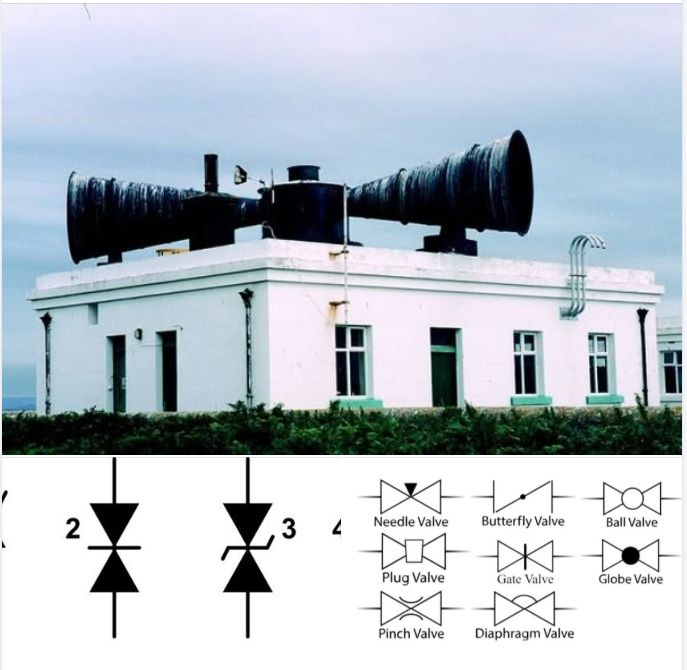
It resembles a voltage-surpressing TVS diode and the symbol for a gate valve.
Another time it reminded me of a phonograph needle tracking the “groove” of a pulsar signal. The symbol becomes a stylus: an instrument sensitive enough to trace modulation, jitter, or non-random deviations in radio stars that could signify intention and an embedded signal within the natural rhythm.

From Point Contact to Quantum Coupling
If energy could circulate endlessly within a torus, then perhaps consciousness did the same – looping through matter, thought, and time in a self-sustaining flow. What if this rhythm could be modeled, even mimicked, in miniature?
Not the universe itself, but its echo: a transistor. Two coupled transistors, facing each other across a thin germanium slab, their currents whispering through the barrier like twin pulses of light – mirrored halves of a cosmic torus, breathing in unison.
Classical to Quantum Transition
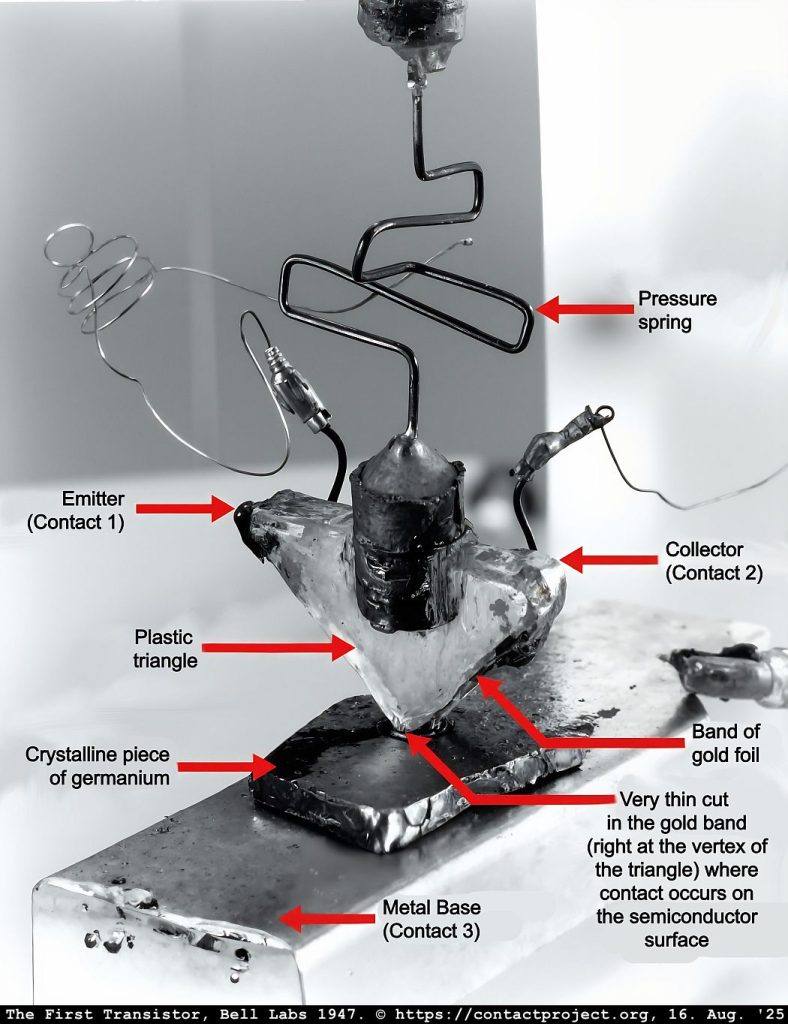
The 1947 point‑contact transistor marked the fragile dawn of modern computing. That first functional transistor, built at Bell Labs in 1947 (Video), marked the birth of the information age – the moment electrons began to speak intelligibly through human design.
Now imagine a second one on the reverse side of the same crystal. Their bases are not separate. They share a heart of germanium, so that when one side breathes, the other side feels it. Amplification and resonance bound together. This was no longer a device of simple on/off switching but a duet.
When Transistor 1 is active, holes injected by its emitter (E₁) form a cloud of positive charge within the germanium. This cloud spreads through the shared base, influencing Transistor 2 below. The extra charge alters its bias conditions, allowing one transistor to modulate or even control the other.
This coupled behavior – one amplifier shaping another – is the essence of the design.
Then came the question that changed everything: what if that germanium block were divided by the thinnest imaginable void – a quantum gap small enough for tunneling?
The Quantum Coupled Transistor (QCT)
By splitting the base with a nanometer-scale barrier, the two halves become physically separate yet quantum-mechanically connected. The bridge between them is no longer conductive matter, but a tunneling junction – a semiconductor–gap–semiconductor structure capable of Negative Differential Resistance (NDR).
The operation of the upper transistor instantly alters the tunneling probability below, coupling the two at femtosecond speeds. In essence, an active quantum device has been embedded at the heart of the transistor pair.
In October 2025, a new realization emerged: replace germanium with graphene, separated by hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). The QCT thus becomes a quantum membrane – a bridge of probability rather than metal, where conduction occurs through resonance, not contact.
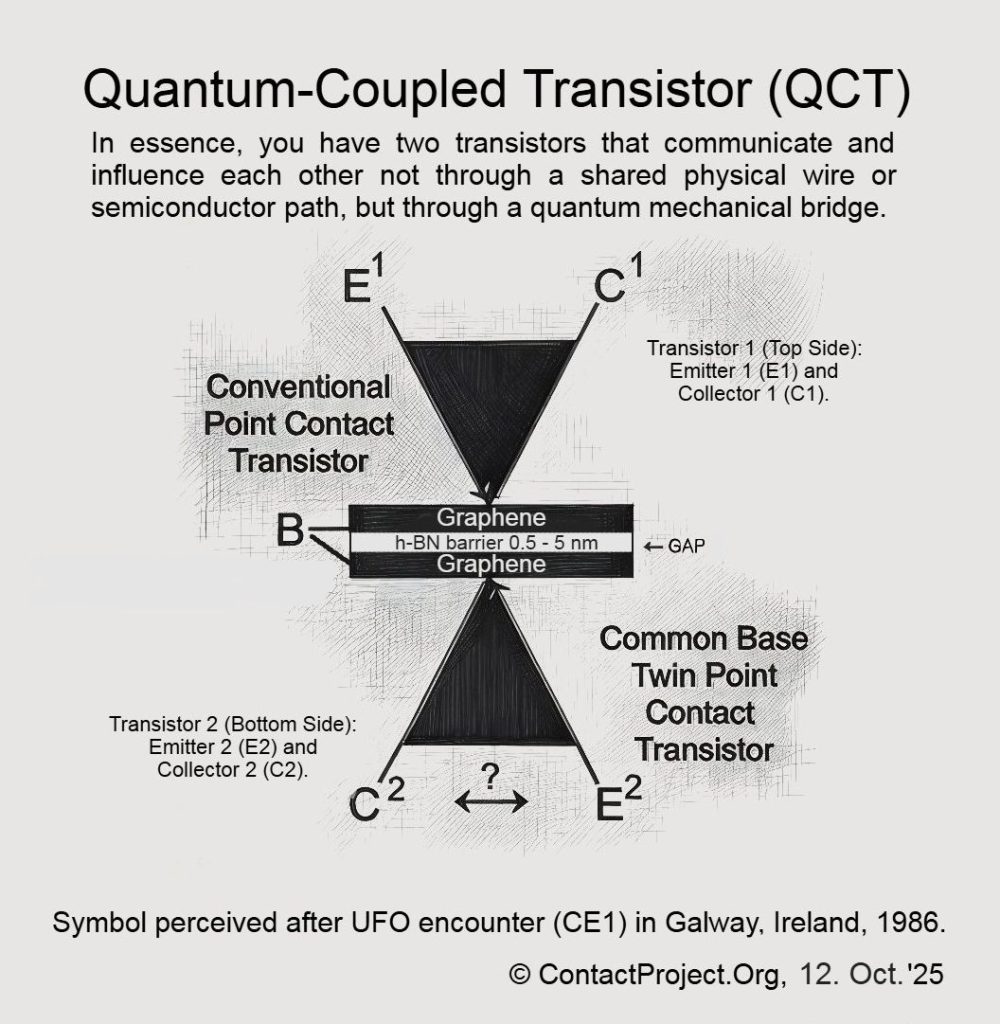
In such a device, matter behaves less like circuitry and more like a standing wave – a field conversing with its own reflection.
Sandia’s 1998 Quantum Transistor vs 1986 Galway UFO Design
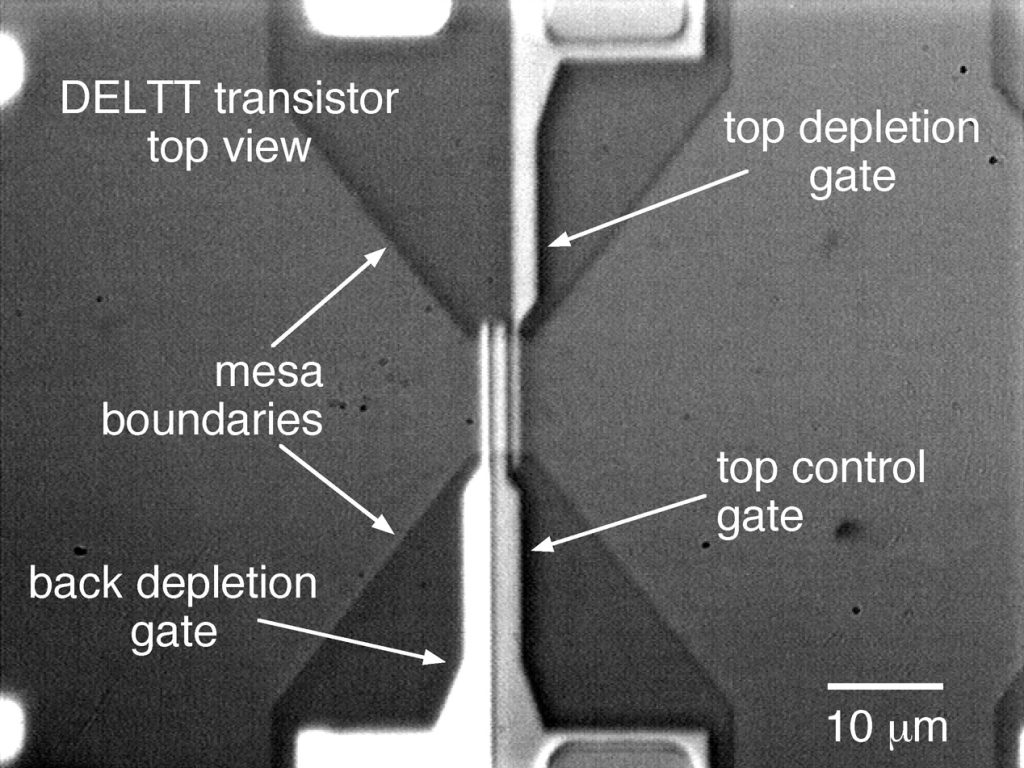
In February 1998, Sandia National Laboratories announced the Double Electron Layer Tunneling Transistor (DELTT) – a revolutionary device built from two vertically stacked transistors separated by a nanometer-thin barrier, allowing electrons to “tunnel” between layers through a quantum bridge.
Compared to Sandia’s 1998 DELTT transistor (~1 THz operation), a graphene–hBN–graphene Quantum Coupled Transistor (QCT) could theoretically reach 10–50 THz (and up to 160 THz intrinsically), with 1–5 THz achievable for cryogenic prototypes.
The Torus and the Transistor
The torus and the QCT share a deep symmetry: both circulate energy through a void, sustained by resonance and feedback.
| Torus Principle | QCT Analogue |
|---|---|
| Continuous flow through a void | Electron tunneling through a nanogap |
| Mutual induction of fields | Charge and potential coupling between transistors |
| Inner and outer circulation | Emitter–collector feedback loops |
| Central void | h-BN or vacuum tunneling barrier |
| Dynamic equilibrium | Negative Differential Resistance (bistability, oscillation) |
In the torus, energy never escapes; it circulates, held in balance by feedback.
In the QCT, charge does the same: injected, tunneled, reabsorbed, and re-emitted in a rhythm as fast as thought – measured not in seconds, but in femtoseconds. The circuit breathes; information moves through the void without crossing it.
And perhaps this is the deeper symmetry: that consciousness, too, circulates like current – capable of coupling across time, of reaching backward through the vacuum between moments. The Challenger dream, the torus vision, the UFO over Galway Bay – each was part of that same feedback cycle, signals in resonance across the years.
Superluminal Echo: The Steinberg-Nimtz Connection
In 1993, physicist Aephraim Steinberg and Paul Kwiat and Raymond Chiao timed photons as they tunneled through optical barriers. What they found defied classical intuition: the photons appeared to emerge from the far side faster than light could have crossed the same space.
The effect, called the Hartman Effect, implied that the photon’s wavefunction was not confined by the barrier at all – it extended through it, its phase evolving nonlocally, as if the particle were already aware of its destination.
Steinberg’s careful analysis maintained that no usable signal outran light. The pulse’s leading edge still obeyed Einstein’s limit. Yet, the phase correlations – the ghostly alignment between entry and exit -were effectively superluminal. The system’s coherence spanned the barrier faster than any classical influence could travel, whispering that information about correlations might not be bound by ordinary spacetime intervals.
Around the same time in the 1990s, physicist Günter Nimtz demonstrated that a modulated microwave signal—famously encoding Mozart’s Symphony No. 40 – appeared to tunnel through a pair of prisms faster than light could travel the same distance in air. The result did not violate relativity; rather, it showed that the evanescent field inside a barrier can transmit phase information faster than the group velocity of light.
These laboratory findings inspired the author’s proposal of the Quantum-Coupled Transistor (QCT): a graphene–hBN–graphene device designed to probe whether such evanescent coupling can be controlled, amplified, or even used to exchange information between two quantum domains.
The Quantum Coupled Transistor (QCT) is a solid-state analog of that same principle. Across its h-BN gap, electrons do not march through matter – they tunnel through probability, their wavefunctions interlocking between graphene layers in a shared evanescent field. Alice’s gate bias modulates that field; Bob’s side responds within femtoseconds – almost instantly, not through classical signals but through phase coherence.
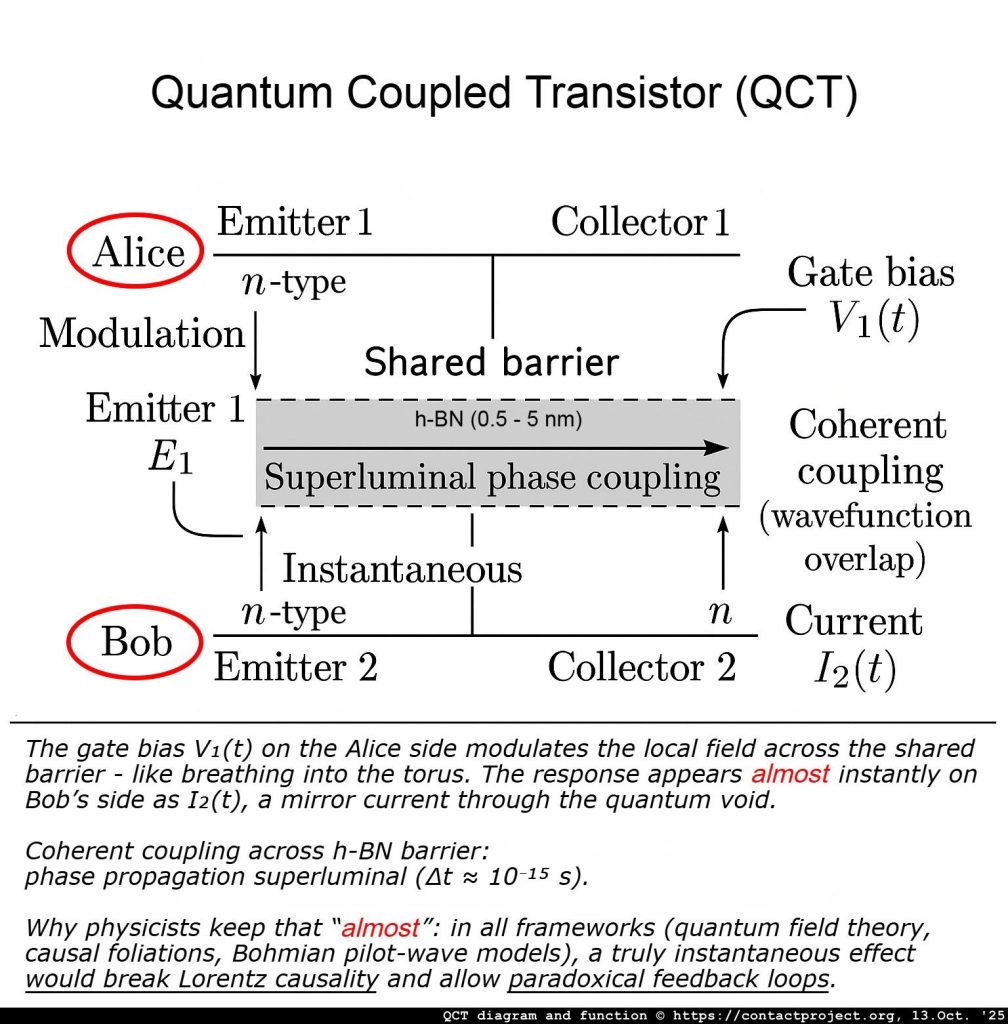
This is Steinberg’s tunneling photon turned electronic – a field coherence that outpaces light yet preserves causality. In an active, nonlinear QCT (biased, resonant, alive,) those same correlations could, in principle, become controllable, carrying information through the void itself.
In that sense, the QCT becomes a technological metaphor for my 1986 experience:
Not prophecy, but phase coherence across the boundary of time –
a superluminal echo, awareness tunneling through the same quantum void that electrons now traverse.
Toward Experimental Verification: The QCT as a Causal Foliation Test Device
In theoretical terms, the QCT embodies a tangible platform for Causal Foliated Signaling (CFS) tests: a medium where phase-linked coherence propagates faster than light yet remains globally consistent. Within such a framework, spacetime is no longer flatly Lorentzian but foliated, like in a book, by hidden simultaneity surfaces – sheets through which superluminal interactions remain orderly, non-paradoxical, and empirically testable.

The Test Setup
Two QCT nodes – Alice and Bob – are fabricated as mirrored graphene–hBN–graphene stacks, each with independent bias control and ultrafast detection. The gate bias on Alice’s side, V1(t), is driven by a pseudorandom terahertz modulation. Bob’s side, isolated and shielded, measures its own tunneling current, I2(t), with femtosecond precision.
The Hypothesis: Causal-Foliated Coupling (CFS)
If conventional quantum theory holds, Bob’s readings remain statistically random.
But if causal-foliated coupling exists – if the evanescent field itself carries structured information – then Bob’s signal will show faint but reproducible cross-correlations synchronized to Alice’s modulation, preceding the classical light-travel delay.
CFS introduces a hidden global time structure (“foliation”) in spacetime.
Within that structure:
- Certain fields (like the QCT’s evanescent tunneling field) can exchange phase information superluminally.
- These exchanges occur along the foliation, preserving causal order globally, even though they appear faster than light locally.
In simpler terms:
There is an underlying “now” in the universe – a hidden simultaneity – along which quantum coherence can propagate.
| Concept | Conventional Quantum Mechanics | Causal-Foliated Coupling |
|---|---|---|
| What Bob sees | Random noise | Faint correlations |
| How Alice affects Bob | Only via light-speed classical channel | Via superluminal phase coupling through evanescent field |
| When effect appears | After c-delay | Before c-delay (aligned with foliation) |
| Causality preserved? | Yes (strictly) | Yes (globally ordered by hidden foliation) |

Rotating the QCT apparatus relative to the cosmic microwave background (CMB) rest frame would test for anisotropy – the telltale fingerprint of a preferred cosmic foliation.
Such an outcome would imply that phase information, not energy, can traverse spacetime faster than light – that the universe permits order across the void, so long as it respects the hidden rhythm of its own higher geometry.
The Closing Symmetry
At the cosmic scale, the torus is the universe breathing through itself.
At the quantum scale, the QCT is electrons tunneling through themselves.
And across time, perhaps consciousness does the same – looping through the void in superluminal resonance, where tomorrow can whisper into yesterday, and the dream becomes the experiment.

Loops through the void – divided yet continuous, speaking across the gap.
Both embody the paradox of separation as communication – the same principle that allowed a future event to echo backward into a dream, and a vision to crystallize, decades later, as a transistor that remembers the shape of the cosmos.
This article is part of a series, all related to an unexplained sighting I had in 1986 in Ireland:
- UFO Over Galway Bay Chapter 1: The 1986 Salthill Encounter
- The Black UFO Report: Prince Charles, a Jumbo Jet, and a Night of Aerial Mysteries
- UFO over Galway Bay Chapter 2: Psychic Mayday from a crashed UFO
- UFO over Galway Bay Chapter 3: The Irish Tuatha Dé Danann as Cosmic Visitors
- UFO Over Galway Bay Chapter 4: Reverse Engineering The Quantum Coupled Transistor
- The Quantum-Coupled Transistor (QCT): Amplifying the Void
- Can Information Travel Faster Than Light – Without Breaking Physics?