Rethinking Astrology’s Scientific Basis
For millennia, we have stared into that inky blackness, into that glittering cosmic abyss, and we have felt a connection. It’s a profound human impulse. To see the stars and wonder: are we a part of that? Are our lives, our destinies, entwined in those celestial patterns? This is the heart of astrology – an idea as ancient as it is persistent.
Sagan’s Twin Paradox
Carl Sagan took a look at this in his landmark series Cosmos. He was a master at applying simple, elegant logic to big claims. He posed a challenge – a beautiful, scientific thought experiment: identical twins.

Born minutes apart in the same place, their astrological charts are virtually indistinguishable. If astrology holds true, their lives should follow similar paths. Yet, as Sagan pointed out, their destinies often diverge wildly. One becomes an artist, the other an accountant. One is happy, one is not. For him, this was proof that astrology didn’t work. Case closed?
Well, not so fast. The universe is always more subtle and interconnected than we first assume.
The Twist in the Tale: Twins Reared Apart
Science, you see, keeps moving. After Sagan’s series, from 1979 to 1999, a groundbreaking study began: The Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart. And the results… wow. They are just jaw-dropping.
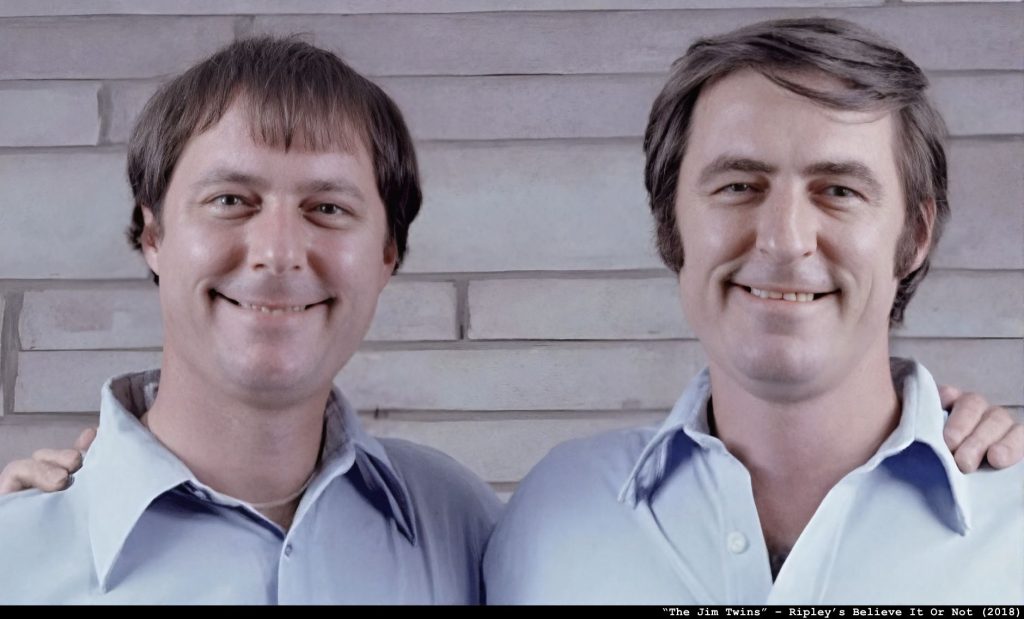

They found pairs of identical twins, separated at birth, who met for the first time as adults and discovered… well, uncanny similarities. The most famous are the “Jim Twins.” Separated at four weeks old. Reunited at 39.
Both had married women named Linda, divorced them, and remarried women named Betty. Both had a son named James. Both owned a dog named Toy. Both drove the same car, smoked the same cigarettes, and even vacationed at the same beach in Florida.
So, what’s going on here? Sagan’s argument was that twins born at the same time have different fates. But here we have evidence that twins born at the same time can have astonishingly similar ones, even when they don’t know each other.
The Ghost in Our Genes… and in the Cosmos?
The mainstream scientific explanation is, of course, genetics. That this is the power of our DNA: the double-helix code as a staggeringly powerful blueprint for who we are. And not just our eye color, but also our temperaments, preferences and predispositions. It’s a fantastic and simple explanation.
The Rise of Epigenetics
But a new field called epigenetics shows that’s not the whole story. Think of your DNA as a giant cookbook. Epigenetics is the master chef who decides which recipes to use based on environmental cues. The cookbook itself doesn’t change, but based on the environment – stress, diet, toxins, love, cold, heat – the chef decides which recipes to use. It adds a little molecular bookmark here, a sticky note there, telling this gene to be loud and that gene to be quiet.

This is why one identical twin can get asthma and the other doesn’t. Their genetic cookbook is identical, but their chefs have made different choices based on different life experiences.
This brings us to the modern case for astrology. If the living cell is an “intelligent system” responding to its environment… what if that environment includes the cosmos? What if the “chef” is, in some small way, listening to the planets?
The Question of Mechanism
Okay. It’s a fascinating idea. So let’s test it.
Scientists have to ask: What is the force? What is the physical mechanism by which Mars – a planet whose gravitational pull on you at birth is less than the pull of the doctor delivering you – can reach into the nucleus of your cell and flip a specific epigenetic switch? Is it gravity? Electromagnetism? The strong or weak nuclear force? Which one? You have to show that a force exists.
Chaos Theory: The Butterfly Effect
How can a distant planet have any effect? This is where we must consider one of the most profound discoveries of modern science: chaos theory.
We’re all familiar with its central metaphor: the “butterfly effect,” where the flap of a butterfly’s wings in Brazil can set off a tornado in Texas. The point is not that the butterfly has the power of a tornado, but that in a complex, dynamic system (like weather, or a human life), a minuscule, barely measurable change in the initial conditions can lead to vastly different outcomes down the line.
The Lyapunov Exponents
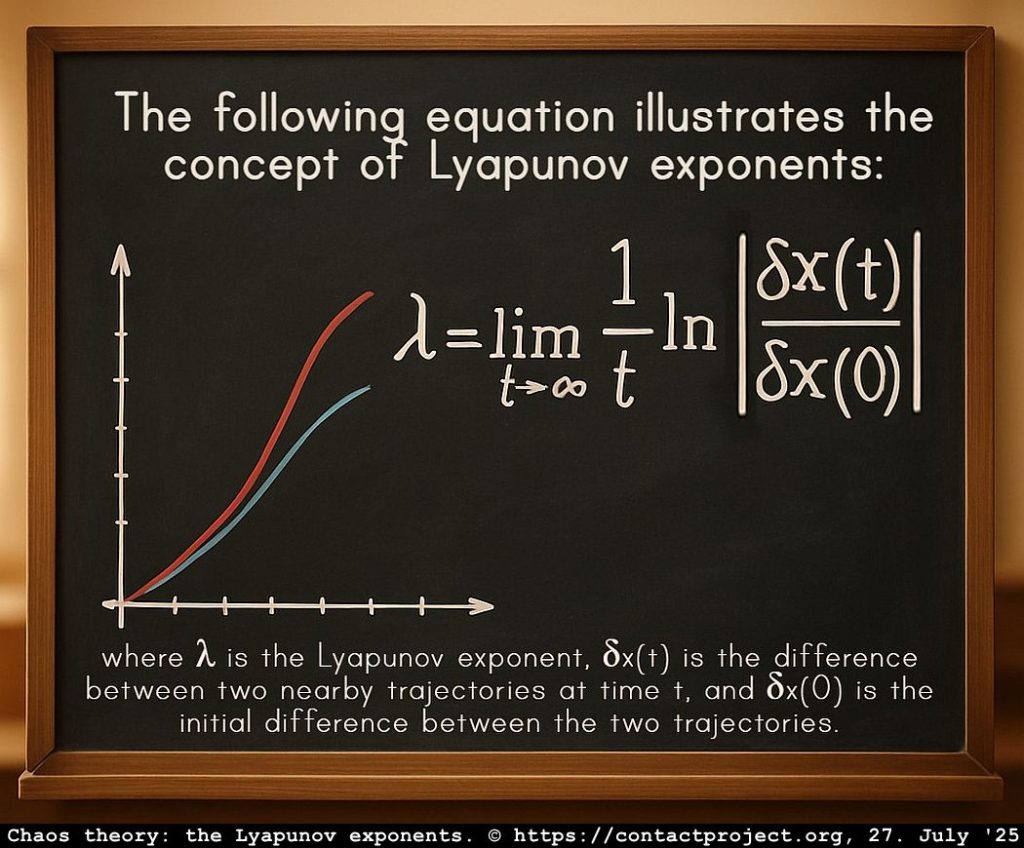
The moment of birth is the ultimate set of “initial conditions” for a human life, the first flutter of possibility, setting the delicate initial conditions that ripple through a life. Like butterfly wings in chaos theory, even the tiniest variations can orchestrate profound destinies.
The Butterfly Wings
This brings us to the modern case for astrology. If the living cell is an “intelligent system” responding to its environment… what if that environment includes the cosmos?
Newsflash: planets already affect life on Earth. Tides, seasons, your vitamin D levels – all cosmic puppetry.
Both gravity and electromagnetic forces can impact genetics by influencing how genes are expressed and how cells function. For example, microgravity conditions can change gene expression patterns related to cell structure, metabolism, and immune responses. Similarly, electromagnetic fields – especially magnetic fields – can also cause changes in gene activity and cell behavior, possibly affecting epigenetic modifications.
For instance gravity: Blaber, E. A., Fogle, H., Dvorochkin, N., Naqvi, S., Lee, C., Yousuf, R., … & Almeida, E. A. (2015). Microgravity induces pelvic bone loss and fatty liver through epigenetic mechanisms. PLoS ONE, 10(4), e0124396.
For instance electromagnetic fields: Cui, Y., Park, J. H., & Miyamoto, Y. (2017). The effect of electromagnetic fields on the epigenetic modifications of DNA and histones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2736.
Planetary Gravity as an Initial Condition
The old rebuttal that the doctor’s gravitational pull is stronger than Mars’s is a failure of imagination. It’s not about raw power. Framed by chaos theory, the subtle gravitational state of the entire solar system at the moment you are born doesn’t need to be strong; it just needs to be the initial “flap of the wings” in the incredibly complex system of your life. We have proof that these tiny forces have huge effects over time: science has confirmed that Mars’s gentle, rhythmic tug is enough to alter Earth’s orbit and drive a 2.4-million-year climate cycle. If that’s not a butterfly causing a planetary-scale tornado, what is?

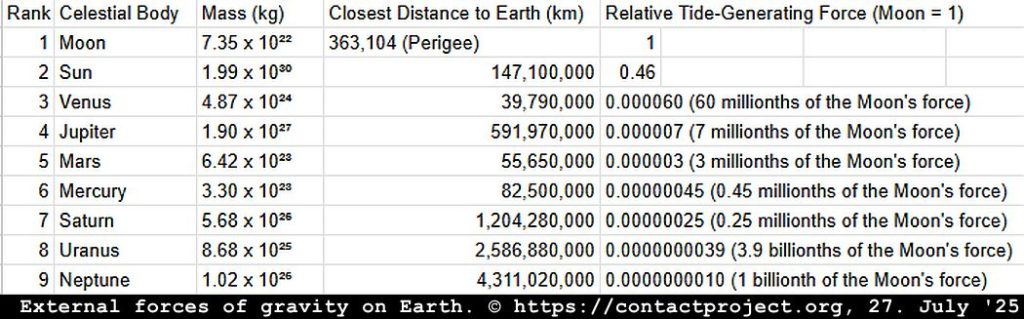
The Moon: Its gravitational pull is so powerful it moves entire oceans, creating the daily tides. This is a tangible, physical force exerted upon the planet and every living thing on it, a rhythmic pulse that has shaped coastal life for eons.
The following table provides a comprehensive comparison of the maximum possible tide-generating force of the Sun and all planets relative to the Moon:
Planetary Electromagnetism as an Initial Condition:
We know planets are not inert. They are dynamic worlds broadcasting unique energetic signatures. Jupiter and Saturn emit powerful radio waves detectable on Earth. These are not brute forces, but tiny variations in the initial electromagnetic environment – part of the unique cosmic “weather pattern” you were born into. They are another set of butterfly wings, flapping at the precise moment your own complex system began its journey.
The Sun: Its cycles govern our seasons, our climate, and the circadian rhythms that are hard-wired into our biology. The Sun’s immense electromagnetic energy literally fuels our world and directly impacts Earth’s magnetic shield. Its influence is total.
The Radio Planets
The following chart details the magnetic moment of each planet – a measure of the magnetic field’s overall strength – relative to Earth’s.
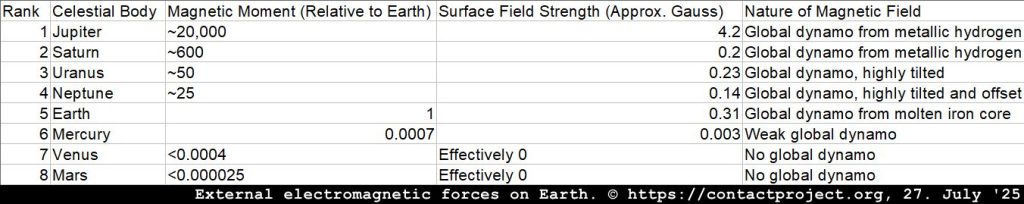
Jupiter‘s powerful magnetosphere accelerates charged particles to incredible energies, producing intense radio waves. These “decametric” radio bursts are so powerful that, at certain frequencies, Jupiter can be the brightest object in the sky after the Sun.
Saturn is a source of intense radio emissions, much like Jupiter. Its auroral radio waves, known as Saturn Kilometric Radiation (SKR), are similar to Jupiter’s but are not powerful enough to be detected by radio telescopes on Earth. However, Saturn produces another, more powerful type of radio signal from massive lightning storms in its atmosphere. These signals, called Saturn Electrostatic Discharges (SEDs), are at least 10,000 times stronger than emissions from terrestrial lightning and have been successfully detected by ground-based radio telescopes.
Uranus and Neptune: The Voyager 2 spacecraft confirmed that both Uranus and Neptune are “radio planets” with complex radio emissions generated by their magnetic fields. However, their radio signals are considerably weaker than those from Jupiter and Saturn. While a tentative detection of Uranus was reported by an Earth-orbiting satellite in the 1970s, the signal was difficult to distinguish from terrestrial interference.
The other rocky planets, Venus and Mars, do not have significant global magnetic fields and are not known to be sources of noticeable radio emissions. However, you will hear radio waves coming from those planets in the following recording:
Our Universe Is Not Silent
All planets in our solar system emit waves, gravitational and electromagnetic. NASA recorded radio waves from planets with the help of spacecraft. They then converted the signals into the audible range of human hearing (20-20,000 Hz). So, you can listen to all planet sounds from space.
A New Cosmic Perspective
I have presented here a number of arguments of why astrology may actually have a scientific basis. Chaos theory explains how small initial differences can have a huge effect. Sagan’s initial argument against serious astrology, is shown to be inconclusive.
There’s a case to be made for the infinitesimal influence of the planets on our DNA, magnified through the Lyapunov exponents.
And I haven’t even touched on the possibility of quantum entanglement of our atoms with the cosmos.
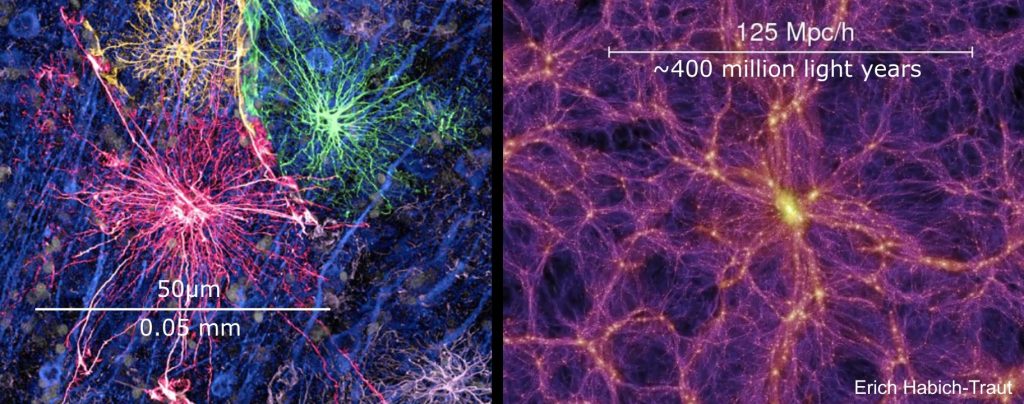
The universe is connected. We are stardust. Now that is a cosmic perspective.
Empirical Evidence
The one characteristic that sets astrology apart from science, and which is cited consistently by sceptics, is the lack of empirical evidence. There are plenty of anecdotes, but quantifiable repeatable evidence?
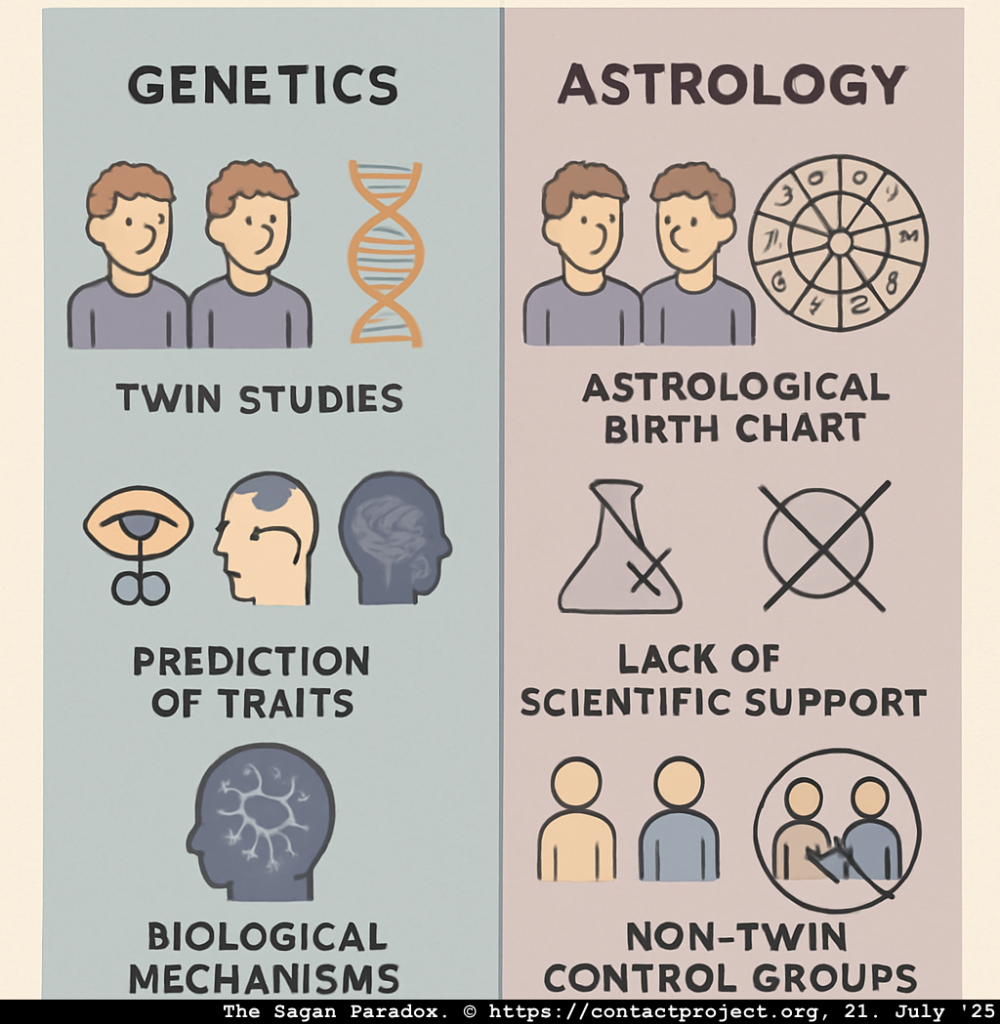
Not so much, apparently.
Of course, I could tell you that I worked in Brussels in 1989 for a NATO defence contractor, and the manager asked me my star sign, and I told him “Aquarius”, upon which he shook his head and told me: ” I knew it. We have 120 employees here, and 80 of them are Aquarius”. Enough with the anecdotes!
I searched around a bit and found this study in a Postgraduate Medical Journal:
Written in the stars: did your specialty choose you?, by Holly Morgan, Hannah Collins, Sacha Moore, and Catherine Eley, 2022.
They surveyed 1,923 physicians in the UK and uncovered some surprisingly specific, and sometimes quirky, correlations between their zodiac signs, personality traits, and the medical fields they chose.
The patterns they found are intriguing:
Physicians specializing in Care of the Elderly were more likely to be Geminis, known for their communication skills, than Cancers (16.1% vs 2.3%).
Heart of a Lion: Cardiologists, who deal with the heart, were far more likely to be Leos. In the study, 14.4% of cardiologists were Leos, compared to just 3.9% who were Aries.
A Womb with a View: Obstetrics and Gynecology was dominated by Pisces. A full 17.5% of OB-GYNs were Pisces, while there were zero doctors in that specialty who were Sagittarius.
The Practical Capricorn: Those in General Medicine were more likely to be Capricorns (10.4%) than their Aquarius colleagues (6.7%).
Addendum
The Cosmic Irony of Sagan’s Birth Chart
I really wanted to do a horoscope of Carl Sagan:
Birth Information:
Name: Carl Edward Sagan
Date of Birth: November 9, 1934
Time of Birth: 5:05 PM (17:05:00)
Place of Birth: Brooklyn, New York, U.S.
I hit a road block because there is no reliable or verifiable source for his exact birth time. Carl Sagan never spoke about it, nor have his relatives.

An Unverified Source
Carl Sagan’s birth time supposedly was 17:05:00, with the singular source cited as ‘765 Notable Horoscopes‘ on the AstroSage website. ‘Notable Horoscopes’ is a book by B.V. Raman, a respected figure in Vedic astrology. This provided an adhoc time and a traceable source: https://www.astrosage.com/celebrity-horoscope/carl-sagan-birth-chart.asp
A Product of Circular Reasoning
But this raises a number of red flags: his birth time is traced back only to a single origin: a compendium of horoscopes created for the practice of astrology, not for historical accuracy. The claim is contradicted by the complete absence of this information in all reliable records, including extensive biographies, institutional archives, Sagan’s personal papers, and accounts from his family.
The specificity of the time suggests it is not a recorded fact but a “rectified” time, calculated backward to fit a preconceived astrological model, rendering it a product of circular reasoning.
The existence of an unverified astrological birth time for Carl Sagan is not merely a piece of biographical trivia; it is a profound and telling irony.
The sole claim for his time of birth -17:05:00- is uncorroborated, without merit, and should be dismissed as a biographical fact.
I was peeved by this. There’s no record of Carl Sagan’s birth time? I decided to dig deeper.
The Search for the Certificate
With the help of “Upwork”, a professional genealogist and the librarian of the Library of Congress I tracked down Carl Sagan’s birth announcement.

It was deposited in the Seth McFarlane collection. But unfortunately the hospital didn’t write the time of Carl’s birth down. And his birth certificate is sealed from the public until 2035, or some such (100 years after his birth).

And there you go. Of course Sagan – the man who spent decades debunking astrology – would ghost us on his own birth time. The cosmic joke writes itself: the astronomer who demanded evidence for the stars’ influence left us no evidence to test his own chart.
But was it only Sagan who is a sceptic of astrology? No, some Christians also have an uneasy time with it… I thought about it briefly, and then found an argument in favour of astrology, related to Christianity, that is hard to dismiss.
The Divine Symphony: A Christian Case for the Stars
While some Christian interpretations of Astrology focus on biblical prohibitions, a deeper reading reveals a more nuanced and even positive relationship between God, the heavens, and humanity. Rather than seeing astrology as a forbidden practice, we can view it as an ancient and intuitive language through which God communicates with all of creation, a truth powerfully demonstrated at the very birth of Christ.

The birth of Christ was not just announced despite astrology; it was announced through it. The journey of the Magi is a powerful testament that no field of human knowledge is outside of God’s reach. The heavens are not a source of pagan fear but a canvas for divine glory. The story powerfully suggests that for those who seek with a sincere heart, the stars themselves will bow and point the way to the true King.
The Heavens Declare the Glory of God
Psalm 19:1 states this beautifully: “The heavens declare the glory of God; the skies proclaim the work of his hands.”
In this light, astrology is not a departure from God but an attempt to listen to what His creation is saying. It is an act of paying attention. Why would God create such a magnificent and orderly celestial clockwork if not for it to hold meaning and purpose?
The Goal Determines the Goodness of the Practice
The biblical prohibitions against “divination” are aimed at idolatry—the act of replacing God with something else. They forbid seeking guidance from the stars instead of God. The Magi, however, did the exact opposite.
The Magi: Honored Heroes of the Faith
The story of the Magi is not a cautionary tale, but a story of honor. These astrologers from the East are the first Gentiles in the Gospel of Matthew to recognize and worship Jesus. They are presented as wise, diligent, and faithful seekers.
God Meets Us Where We Are
A loving God communicates with people in a language they can understand. He spoke to fishermen in terms of fishing (“I will make you fishers of men”) and to farmers through parables of sowing seeds. To the Magi, who dedicated their lives to reading the heavens, God spoke through a Star.
A Divine Endorsement: By placing a special star in the sky, God was not setting a trap; He was validating their search. He affirmed that their study of the cosmos was a legitimate path that could lead to Him. The Star of Bethlehem can be seen as God’s ultimate seal of approval on the search for divine truth within the patterns of creation.